Stop Ignoring Qualitative Feedback & Start Analyzing It

Quantitative and qualitative customer feedback are both valuable sources of business data, and yet most qualitative data goes unused.
Quantitative data is easier to measure because it’s represented in the form of numerical data. But qualitative data is descriptive – often containing ideas and opinions – and can’t be quantified in the same way as numerical data. First, it needs to be analyzed and structured using advanced data analysis techniques, which we’ll explore later on in this post.
Both quantitative and qualitative data are valuable sources of customer feedback: quantitative data provides a birds-eye view of your business, while qualitative data digs into customer comments and their personal feelings, helping you to truly understand your customers’ needs.
In this post, we’ll help you understand the main differences between the two types of customer feedback, the benefits of each one, and why you can no longer ignore your qualitative customer feedback.
- What Is Quantitative Feedback?
- What Is Qualitative Feedback?
- How to Analyze Qualitative Feedback?
- Qualitative Vs Quantitative Feedback: Which Is Best?
What Is Quantitative Feedback?
Quantitative feedback is customer data that provides numerical results. It helps you quantify aspects of your business, like customer service performance, product success, campaign success, and much more.
Insights are clear-cut, presented as numbers or counts, and can easily be transformed into charts and graphs for even easier analysis.
Quantitative feedback is the most popular method for businesses to measure performance because the rules and tools for quantitative analysis are well established, but there are many other benefits of quantitative feedback that make it a valuable business asset.
Benefits of Quantitative Feedback
- It’s objective. Quantitative data rules out deliberate bias because anyone with access to the same data can check and verify the results.
- Easy to analyze: Quantitative responses can easily be analyzed using simple statistical analysis tools like Excel, making quantitative analysis accessible to everyone.
- Quick to collect. Quantitative feedback is often a product of multiple-choice questions from Net Promoter Score (NPS or Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) surveys, which means it’s usually quick and easy to collect. Respondents can often send their answers with just one click.
- Easy to visualize and spot trends. It’s easy to track quantitative feedback over time (on a weekly, monthly, or quarterly basis), and visualize it in dashboards to spot any sudden changes.
While quantitative feedback is a great starting point to gauge what’s going on in your business, it doesn’t explain the whole story. That’s why it’s important to back up your quantitative analysis results with qualitative feedback analysis.

What Is Qualitative Feedback?
Qualitative feedback is non-numerical information that measures opinions and views from an individual perspective.
Qualitative feedback is used by businesses to gain a deep understanding of customer issues or motivations. It helps them discover the ‘why’ behind quantitative results.
For example, why has a customer left a low customer satisfaction score? Qualitative data goes beyond mere statistics, to provide detailed insights that can lead to product, service, and overall business improvements. It’s found in open-ended survey responses, emails, social media conversations, and other unstructured data types – from a company’s internal systems’ data or all over the internet.
While qualitative feedback is harder to analyze than quantitative data, you’ll gain detailed customer insights that will help you make key business decisions. And with low-code tools like MonkeyLearn making it easier than ever to analyze qualitative feedback, now is the time to stop ignoring it and start making use of it.
Benefits of Qualitative Feedback
- More detailed customer insights: Qualitative feedback helps you better understand your customers, and learn how they feel about specific aspects of your company. It may appear painful to analyze at first, but really digging into negative customer feedback often provides the most useful insights.
- Open and honest feedback: Open-ended questions prompt more honest responses that offer more insight, and respondents aren’t inadvertently led in any particular direction.
- New ideas Customers will often request new features and leave recommendations in open-ended responses, generating new ideas and suggestions for your product managers.
Qualitative feedback helps businesses become more customer-centric. By continuously listening to the voice of the customer and understanding where you need to improve, you’ll begin to see exponential growth.
However, you’ll need to make sure that your qualitative results are accurate, which depends on the skills and integrity of the person carrying out the qualitative analysis, as well as the performance of the tools you use.
How to Analyze Qualitative Feedback?
It’s likely that you already have a repeatable process and tools in place for analyzing your quantitative feedback. But how can you extract insights from your qualitative feedback?
Low-code NLP tools, like MonkeyLearn, are going mainstream and making it easier than ever to analyze qualitative feedback.
MonkeyLearn provides a suite of ready-to-use text analysis tools that help you mine huge amounts of qualitative feedback in next to no time. You can use sentiment analysis to automatically detect emotions in your data, or topic analysis to discover which aspects of your business customers mention most often. Other capabilities, like keyword extraction, are useful to highlight common words or themes within your data or summarize whole texts.
Combine all of these tools together for powerful data analysis, exceptional accuracy, and instantly actionable insights with MonkeyLearn Studio.
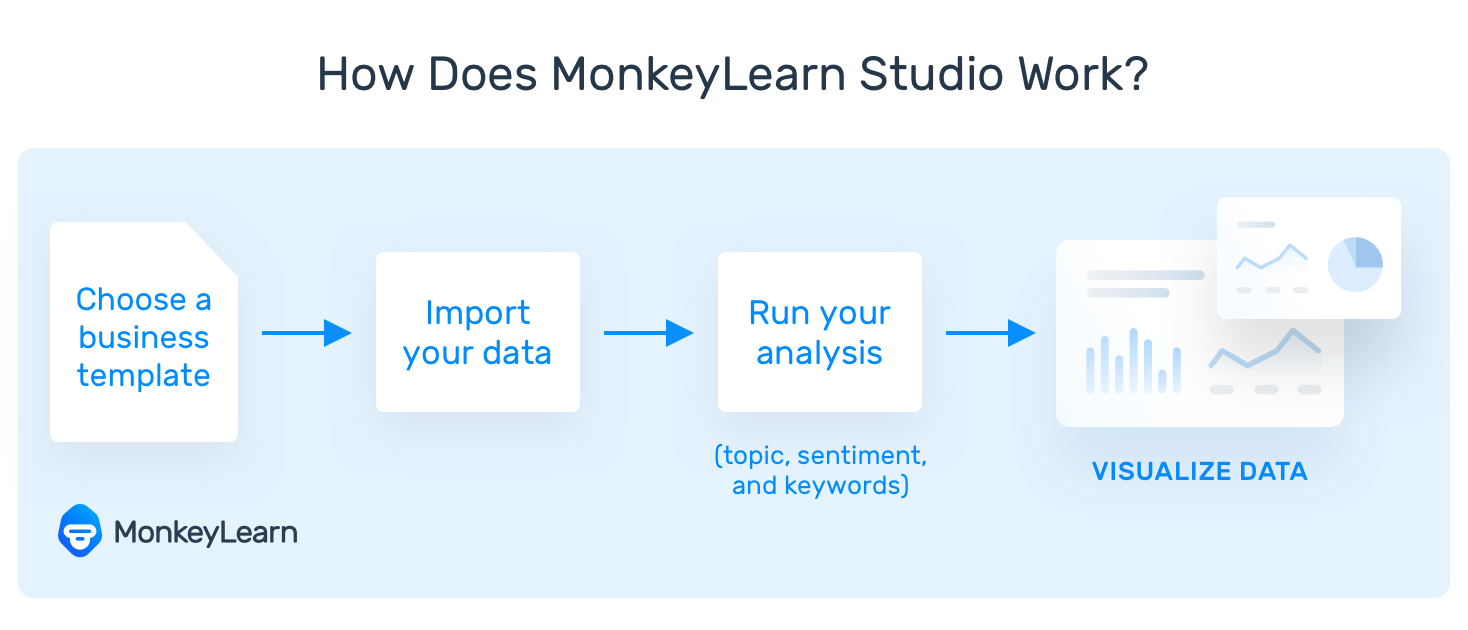
This all-in-one text analysis and data visualization solution provides a template for all types of qualitative data, whether social media, reviews, surveys, or email, and automatically runs your data through each analysis technique (topic, sentiment, and keywords).
Finally, results are displayed in a striking dashboard, so you can easily spot trends and patterns in the same way you would with quantitative data.
Sign up to MonkeyLearn to start analyzing your qualitative data. And connect your data via MonkeyLearn’s robust API or using one of the many available integrations. You can also collect your data in a CSV or Excel file and upload directly to MonkeyLearn’s text analysis models.
So, Qualitative Vs Quantitative Feedback: Which Is Best?
Each type of feedback serves a different purpose. Quantitative feedback is a great option if you need quick results that provide an overview of your business or a particular aspect. Qualitative feedback, on the other hand, delivers more detailed insights that lead to improved customer experiences and better decision-making.
Qualitative and quantitative data are supportive of each other, so it’s best to perform both a quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Now, with easy-to-use text analysis tools, there’s no excuse for not analyzing your qualitative feedback. Sign up to MonkeyLearn to try out our tools for yourself, or schedule a demo and we’ll walk you through how to analyze your qualitative data.

Tobias Geisler Mesevage
January 20th, 2021






