What Is Natural Language Processing
Businesses are inundated with unstructured data, and it’s impossible for them to analyze and process all this data without the help of Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Read on to learn what natural language processing is, how NLP can make businesses more effective, and discover popular natural language processing techniques and examples. Finally, we’ll show you how to get started with easy-to-use NLP tools.
- What Is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
- Why Is Natural Language Processing Important?
- How Does Natural Language Processing Work?
- Natural Language processing Examples
- Natural Language Processing Applications
- Natural Language Processing Tools
Let’s jump into NLP!
What Is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI). It helps machines process and understand the human language so that they can automatically perform repetitive tasks. Examples include machine translation, summarization, ticket classification, and spell check.
Take sentiment analysis, for example, which uses natural language processing to detect emotions in text. This classification task is one of the most popular tasks of NLP, often used by businesses to automatically detect brand sentiment on social media. Analyzing these interactions can help brands detect urgent customer issues that they need to respond to right away, or monitor overall customer satisfaction.
Why Is Natural Language Processing Important?
One of the main reasons natural language processing is so critical to businesses is that it can be used to analyze large volumes of text data, like social media comments, customer support tickets, online reviews, news reports, and more.
All this business data contains a wealth of valuable insights, and NLP can quickly help businesses discover what those insights are.
It does this by helping machines make sense of human language in a faster, more accurate, and more consistent way than human agents.
NLP tools process data in real time, 24/7, and apply the same criteria to all your data, so you can ensure the results you receive are accurate – and not riddled with inconsistencies.
Once NLP tools can understand what a piece of text is about, and even measure things like sentiment, businesses can start to prioritize and organize their data in a way that suits their needs.
Challenges of NLP
While there are many challenges in natural language processing, the benefits of NLP for businesses are huge making NLP a worthwhile investment.
However, it’s important to know what those challenges are before getting started with NLP.
Human language is complex, ambiguous, disorganized, and diverse. There are more than 6,500 languages in the world, all of them with their own syntactic and semantic rules.
Even humans struggle to make sense of language.
So for machines to understand natural language, it first needs to be transformed into something that they can interpret.
In NLP, syntax and semantic analysis are key to understanding the grammatical structure of a text and identifying how words relate to each other in a given context. But, transforming text into something machines can process is complicated.
Data scientists need to teach NLP tools to look beyond definitions and word order, to understand context, word ambiguities, and other complex concepts connected to human language.
How Does Natural Language Processing Work?
In natural language processing, human language is separated into fragments so that the grammatical structure of sentences and the meaning of words can be analyzed and understood in context. This helps computers read and understand spoken or written text in the same way as humans.
Here are a few fundamental NLP pre-processing tasks data scientists need to perform before NLP tools can make sense of human language:
- Tokenization: breaks down text into smaller semantic units or single clauses
- Part-of-speech-tagging: marking up words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, etc
- Stemming and lemmatization: standardizing words by reducing them to their root forms
- Stop word removal: filtering out common words that add little or no unique information, for example, prepositions and articles (at, to, a, the).
Only then can NLP tools transform text into something a machine can understand.
The next step is to build an NLP algorithm.
Natural Language Processing Algorithms
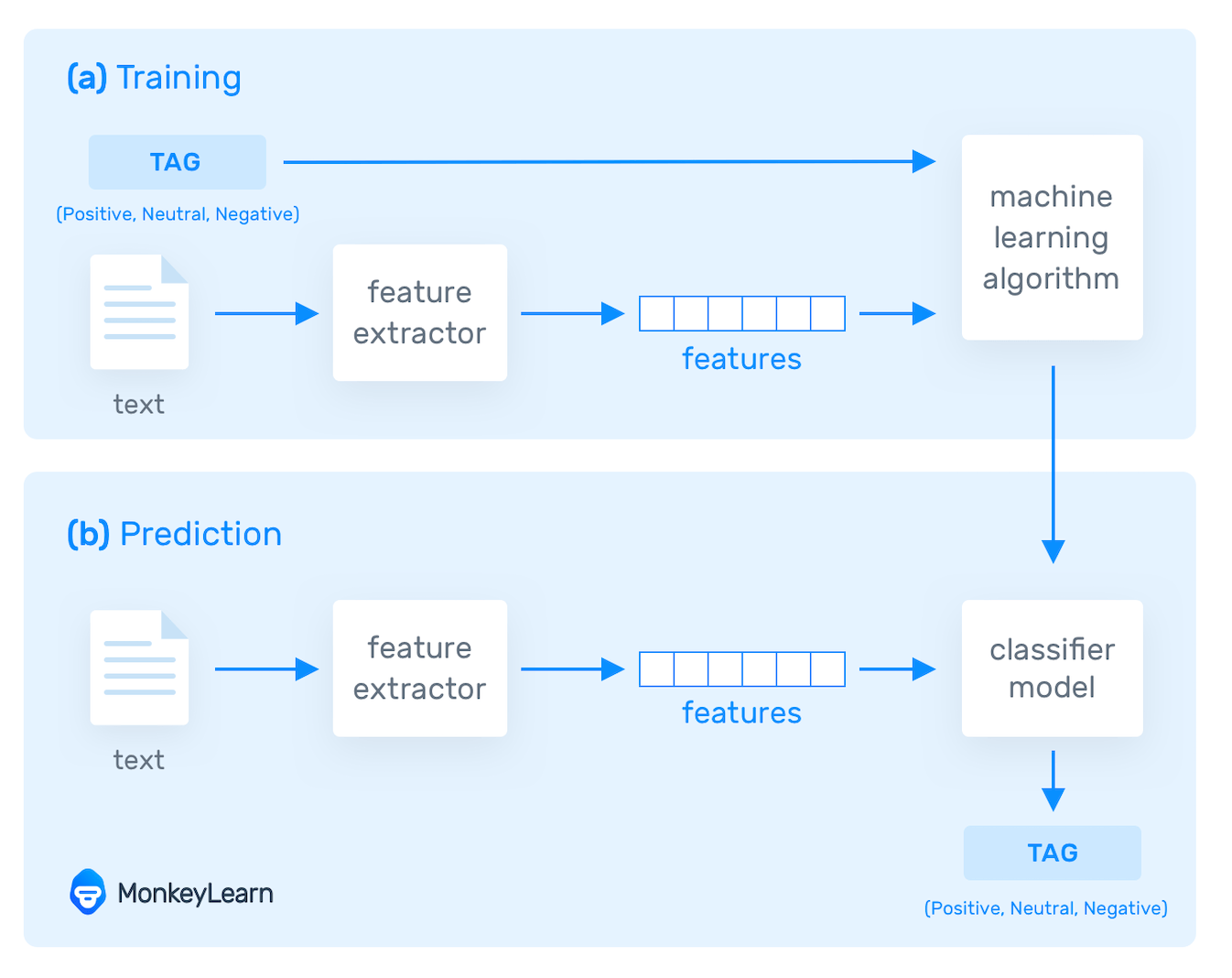
Once your data has been pre-processed, it’s time to move onto the next step: building an NLP algorithm, and training it so it can interpret natural language and perform specific tasks.
There are two main algorithms you can use to solve NLP problems:
A rule-based approach. Rule-based systems rely on hand-crafted grammatical rules that need to be created by experts in linguistics, or knowledge engineers. This was the earliest approach to crafting NLP algorithms, and it’s still used today.
Machine learning algorithms. Machine learning models, on the other hand, are based on statistical methods and learn to perform tasks after being fed examples (training data).
The biggest advantage of machine learning algorithms is their ability to learn on their own. You don’t need to define manual rules – instead machines learn from previous data to make predictions on their own, allowing for more flexibility.
Machine learning algorithms are fed training data and expected outputs (tags) to train machines to make associations between a particular input and its corresponding output. Machines then use statistical analysis methods to build their own “knowledge bank” and discern which features best represent the texts, before making predictions for unseen data (new texts):
Natural Language Processing Examples
Natural Language Processing enables you to perform a variety of tasks, from classifying text and extracting relevant pieces of data, to translating text from one language to another and summarizing long pieces of content.
Text Classification
Text classification is one of the most basic NLP tasks and consists of assigning categories (tags) to a text, based on its content. Classification models can serve different purposes, for example:
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is the process of analyzing emotions within a text and classifying them as positive, negative, or neutral. By running sentiment analysis on social media posts, product reviews, NPS surveys, and customer feedback, businesses can gain valuable insights about how customers perceive their brand.Take these Zoom customer and product reviews, for example:
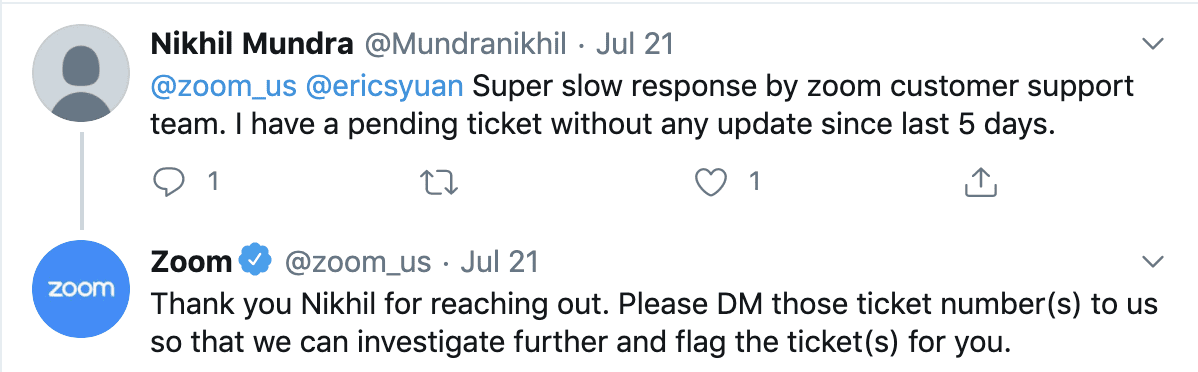

Equipped with natural language processing, a sentiment classifier can understand the nuance of each opinion and automatically tag the first review as Negative and the second one as Positive. Imagine there’s a spike in negative comments about your brand on social media; sentiment analysis tools would be able to detect this immediately so you can take action before a bigger problem arises.
Topic Classification
Topic classification consists of identifying the main themes or topics within a text and assigning predefined tags. For training your topic classifier, you’ll need to be familiar with the data you’re analyzing, so you can define relevant categories. For example, you might work for a software company, and receive a lot of customer support tickets that mention technical issues, usability, and feature requests.In this case, you might define your tags as Bugs, Feature Requests, and UX/IX.
Intent Detection
Intent detection consists of identifying the purpose, goal, or intention behind a text. It’s an excellent way of sorting outbound sales email responses by Interested, Need Information, Unsubscribe, Bounce, etc. The tag Interested could help you spot a potential sale opportunity as soon as an email enters your inbox!
Text Extraction
Another example of NLP is text extraction, which consists of pulling out specific pieces of data that are already present in a text. It’s a perfect way to automatically summarize text or find key information. The most common examples of extraction models are:
Keyword Extraction
Keyword extraction automatically extracts the most important words and expressions within a text. This can provide you with a sort of preview of the content and its main topics, without needing to read each piece. Check out this feature request, below, processed with MonkeyLearn’s public keyword extractor:
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
Named Entity Recognition (NER) allows you to extract the names of people, companies, places, etc. from your data.
Machine Translation
This was one of the first problems addressed by NLP researchers. Online translation tools (like Google Translate) use different natural language processing techniques to achieve human-levels of accuracy in translating speech and text to different languages. Custom translators models can be trained for a specific domain to maximize the accuracy of the results.
Topic Modeling
Topic modeling is similar to topic classification. This example of natural language processing finds relevant topics in a text by grouping texts with similar words and expressions.
Since you don’t need to create a list of predefined tags or tag any data, it’s a good option for exploratory analysis, when you are not yet familiar with your data.
Natural Language Generation (NLG)
Natural language generation, NLG for short, is a natural language processing task that consists of analyzing unstructured data and using it as an input to automatically create content.
It can be used to generate automated answers, write emails, and even books!
Natural Language Processing Applications
Natural language processing allows businesses to make sense of unstructured data ― like emails, social media posts, product reviews, online surveys, and customer support tickets ― and gain valuable insights to enhance their decision-making processes. Companies are also using NLP to automate routine tasks, reducing times and costs, and ultimately becoming more efficient.
Here are some examples of how businesses are putting NLP into practice:
Automatically Analyze Customer Feedback
Analyzing customer feedback is essential to know what clients think about your product. However, this data may be difficult to process. NLP can help you leverage qualitative data from online surveys, product reviews, or social media posts, and get insights to improve your business.
For example, NPS surveys are often used to measure customer satisfaction. First, customers are asked to score a company from 0 to 10 based on how likely they are to recommend it to a friend (low scorers are categorized as Detractors, average scorers as Passives and high scorers as Promoters); then, an open-ended follow-up question asks customers the reasons for their score.
Using an NLP topic classifier, you can tag each open-ended response with categories like like Product UX, Customer Support, Ease of Use, etc. Then, further categorize this data into Promoters, Detractors, and Passives, to see which topics are most prevalent within each group:
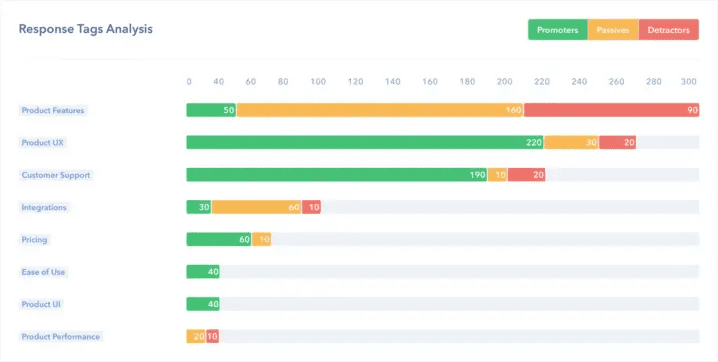
In this example, above, the results show that customers are highly satisfied with aspects like Ease of Use and Product UX (since most of these responses are from Promoters), while they’re not so happy with Product Features.
Automate Customer Support Tasks
Businesses are using NLP models to automate tedious and time-consuming tasks in areas like customer service. This results in more efficient processes, and agents with more time to focus on what matters most: delivering outstanding support experiences.
Customer service automation powered by NLP includes a series of processes, from routing tickets to the most appropriate agent, to using chatbots to solve frequent queries. Here are some examples:
Text classification models allow companies to tag incoming support tickets based on different criteria, like topic, sentiment, or language, and route tickets to the most suitable pool of agents. An e-commerce company, for example, might use a topic classifier to identify if a support ticket refers to a shipping problem, missing item, or return item, among other categories.
Classifiers can also be used to detect urgency in customer support tickets by recognizing expressions such as ‘ASAP, immediately, or right now’, allowing agents to tackle these first.
Here’s an example of how you can use MonkeyLearn’s urgency detector to spot an issue that needs to be solved right away
- Customer support teams are increasingly using chatbots to handle routine queries. This reduces costs, enables support agents to focus on more fulfilling tasks that require more personalization, and cuts customer waiting times.
Top NLP Tools to Help You Get Started
Natural language processing is one of the most complex fields within artificial intelligence. But, trying your hand at NLP tasks like sentiment analysis or keyword extraction needn’t be so difficult. There are many online NLP tools that make language processing accessible to everyone, allowing you to analyze large volumes of data in a very simple and intuitive way.
SaaS platforms are great alternatives to open-source libraries, since they provide ready-to-use solutions that are often easy to use, and don’t require programming or machine learning knowledge.
If you want to integrate tools with your existing tools, most of these tools offer NLP APIs in Python (requiring you to enter a few lines of code) and integrations with apps you use every day.
6 of the Best SaaS NLP Tools:
The NLP tool you choose will depend on which one you feel most comfortable using, and the tasks you want to carry out.
For example, MonkeyLearn offers a series of offers a series of no-code NLP tools that are ready for you to start using right away.
Once you get the hang of these tools, you can build a customized machine learning model, which you can train with your own criteria to get more accurate results.
Check out these tutorials once you’re ready to start building your own custom NLP model:
Final Words on Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing is one of the most promising fields within Artificial Intelligence, and it’s already present in many applications we use on a daily basis, from chatbots to search engines.
Thanks to NLP, businesses are automating some of their daily processes and making the most of their unstructured data, getting actionable insights that they can use to improve customer satisfaction and deliver better customer experiences.
Despite being a complex field, NLP is becoming more and more accessible to users thanks to online tools like MonkeyLearn, which make it simple to create customized models for tasks like text classification and text extraction.
Want to see how it works? Contact us and request a personalized demo from one of our experts.

Rachel Wolff
February 26th, 2020